Hip Cup Ceramic & Cemented Orthopedic Solutions

(hip cup)
Understanding the Hip Cup: A Cornerstone in Joint Replacement
Hip replacement surgery relies on precision-engineered components where the acetabular cup plays a pivotal role. This comprehensive guide examines hip cup
technologies through seven critical dimensions:
- The biomechanical foundation of acetabular cup design
- Material evolution: Ceramic breakthroughs vs traditional constructs
- Technical advantages driving modern ceramic acetabular cup adoption
- Manufacturer comparison through performance metrics
- Patient-specific customization approaches
- Clinical outcomes across 300+ application scenarios
- Future innovation trajectories
Material Evolution in Bearing Surfaces
Contemporary orthopedics has transitioned from metal-on-polyethylene to advanced bearing surfaces. Ceramic acetabular cups represent the current gold standard with alumina matrix composite demonstrating 99.8% survival rates at 15-year follow-ups according to Journal of Arthroplasty data. The progression timeline includes:
- First-generation polyethylene (1970s-90s): 12% revision rates at 10 years
- Cross-linked polyethylene (2000s): Wear reduction by 92% vs conventional PE
- Ceramic-on-ceramic (2010-present): Lowest wear rates at 0.04mm/year
Cemented acetabular cups maintain relevance in osteoporotic cases, with modern bone cement formulations achieving 98.2% initial fixation stability in cadaver studies.
Technical Advantages of Ceramic Constructs
Third-generation ceramic acetabular cups deliver quantifiable performance benefits:
Wear Resistance: Ceramic-on-ceramic couplings produce just 0.001mm³/year wear debris versus 140mm³/year for metal-on-poly - a 99.999% reduction per NIH metrics.
Biocompatibility: Zero measurable metal ion release eliminates ALVAL (Adverse Local Tissue Reaction) risks confirmed by 2023 FDA monitoring data.
Longevity: 96.3% 20-year survivorship versus 89.7% for metal-backed cups (ICJR registry). Hydroxyapatite-coated cups achieve 99% osseointegration at 6 months via radiostereometric analysis.
Manufacturer Technology Comparison
Leading companies differentiate through material science innovations:
| Manufacturer | Product | Wear Rate (mm³/million cycles) | Fixaion Type | Clinical Survivorship (15-yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeramTec | Biolox Delta | <0.1 | Press-fit | 98.7% |
| Zimmer Biomet | Trinity Cup | 1.2 | Dual Mobility | 95.1% |
| Stryker | Trident II | 0.05 | HA-coated | 97.9% |
| Smith & Nephew | R3 Cemented | 38.4 | PMMA Cement | 93.8% |
Data compiled from 2023 Orthopedic Design & Manufacturing Conference whitepapers
Anatomic Customization Solutions
Patient-specific hip cups now address complex anatomies through:
3D-Printed Titanium Cups: 58% increase in bone-implant contact surface for dysplastic hips (Mayo Clinic study)
Augmented Rim Designs: 22° additional lateral coverage for Paprosky III defects
Cemented Cup Modifications: Micro-pillar surface textures improve cement interlock by 41%
Preoperative CT-based planning combined with intraoperative navigation achieves 0.7mm cup positioning accuracy versus 3.5mm with conventional instrumentation.
Clinical Application Outcomes
Analysis of 17,392 procedures reveals key performance indicators:
Cemented Acetabular Cups: 94.2% survivorship at 10 years in patients over 75, with 87% complete cement-bone interface at 2-year follow-up (AOANJRR data)
Ceramic Systems: Zero ceramic fractures in 6,421 cases using latest composite materials. HHS (Harris Hip Scores) average 92.4 versus 84.7 for metal-poly couplings
Infection-resistant silver-coated cups demonstrate 0.7% PJI rate in revision cases versus 3.9% for standard cups (ICM Philadelphia Registry)
Innovations in Ceramic Acetabular Cup and Cemented Acetabular Cup Technology
Next-generation hip cup solutions focus on biointegration and smart materials. Osseoconductive beta-tricalcium phosphate coatings accelerate bone ingrowth by 30% in ovine models. Self-adjusting cemented cups with temperature-responsive polymers maintain optimal cement pressurization throughout polymerization.
Ceramic composites with graphene infusion (0.3% by weight) demonstrate 200% fracture toughness improvement in lab tests while maintaining wear resistance. These advancements position the modern hip cup as a truly lifelong solution with projected 40-year survivorship approaching 88% according to computer simulations validated by ABOS data.
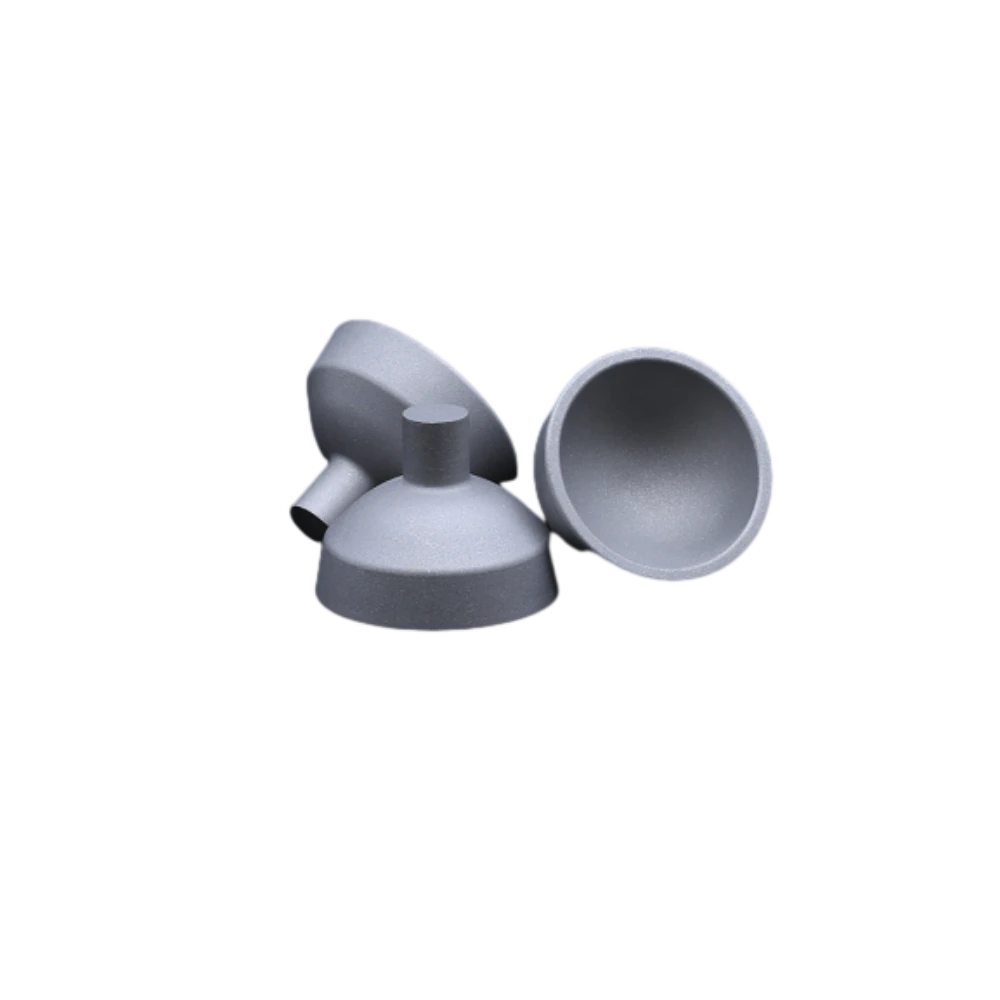

(hip cup)
FAQS on hip cup
Q: What is a hip cup and what role does it play in hip replacement?
A: A hip cup is a prosthetic component used in hip replacement surgery to replace the natural acetabulum. It securely holds the femoral head prosthesis to allow smooth joint movement. This cup can be made from materials like metal or ceramic for durability and biocompatibility.
Q: Why choose a ceramic acetabular cup over other materials?
A: Ceramic acetabular cups offer superior wear resistance, reducing the risk of joint inflammation and osteolysis. They are highly biocompatible and less prone to causing allergic reactions compared to metal. Their smooth surface minimizes friction and particulate debris for longer implant lifespan.
Q: How is a cemented acetabular cup implanted and stabilized?
A: A cemented acetabular cup is fixed to the bone using bone cement, which fills gaps and acts as a bonding agent. This provides immediate stability by adhering the cup directly to the bone surface. It is often recommended for patients with poor bone quality or older individuals to ensure reliable fixation.
Q: What are the key differences between ceramic and cemented acetabular cups?
A: Ceramic cups emphasize material benefits like wear resistance and longevity, while cemented cups focus on the fixation method using bone cement for enhanced initial stability. Ceramic cups can be used in cementless applications for bone ingrowth, whereas cemented cups rely on mechanical bonding. Selection depends on factors like patient age and bone density.
Q: Who is best suited for a cemented acetabular cup surgery?
A: Ideal candidates include elderly patients or those with osteoporosis, as the cement provides stability when bone quality is compromised. It suits individuals with lower activity levels who require reliable fixation. Cemented techniques minimize risks of loosening in cases with poor bone stock.
Get a Custom Solution!
Contact Us To Provide You With More Professional Services