Acetabular Cup: A Core Stabilizing Device in Joint Replacement Surgery
In hip replacement surgery, the Acetabular Cup, as a key prosthesis to replace the human hip socket, is the core component for achieving joint function reconstruction. It was specifically developed to meet the strict requirements of stability, wear resistance, and flexibility in surgery, and its performance directly affects the functional recovery and service life of the hip joint after surgery.

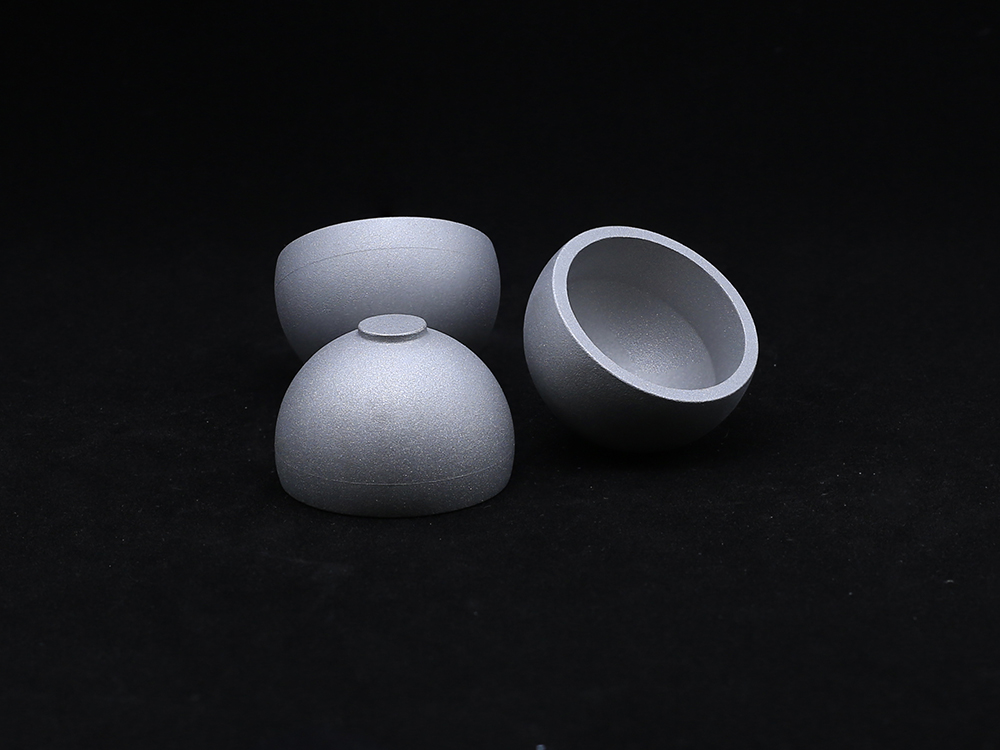
The design of the acetabular cup fully considers the anatomical morphology of the human acetabulum
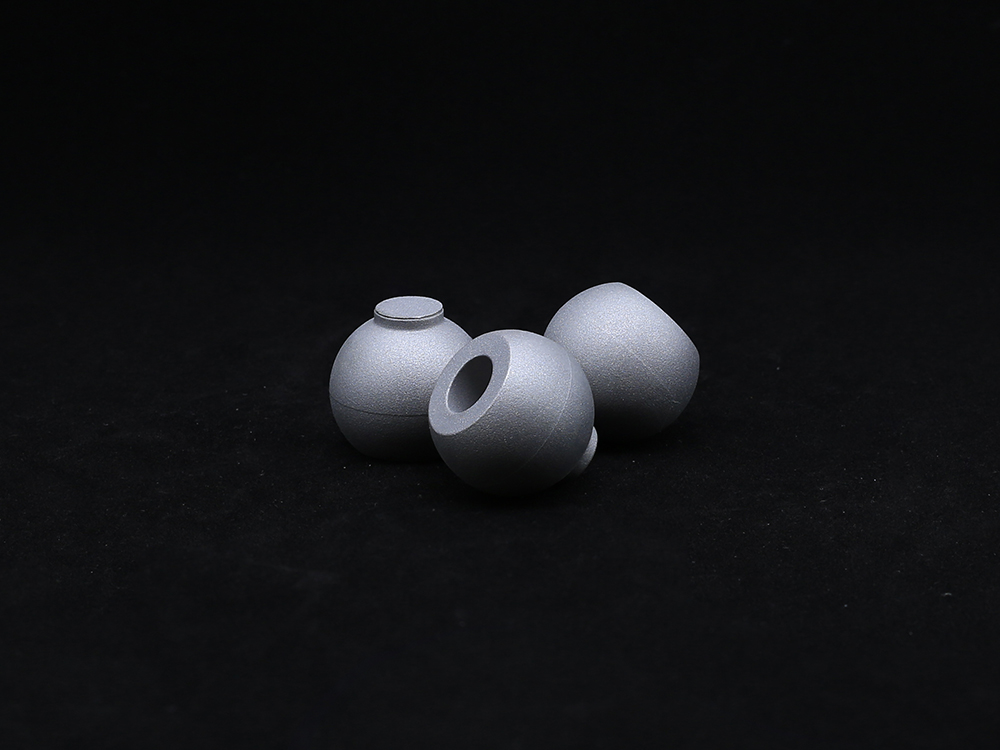
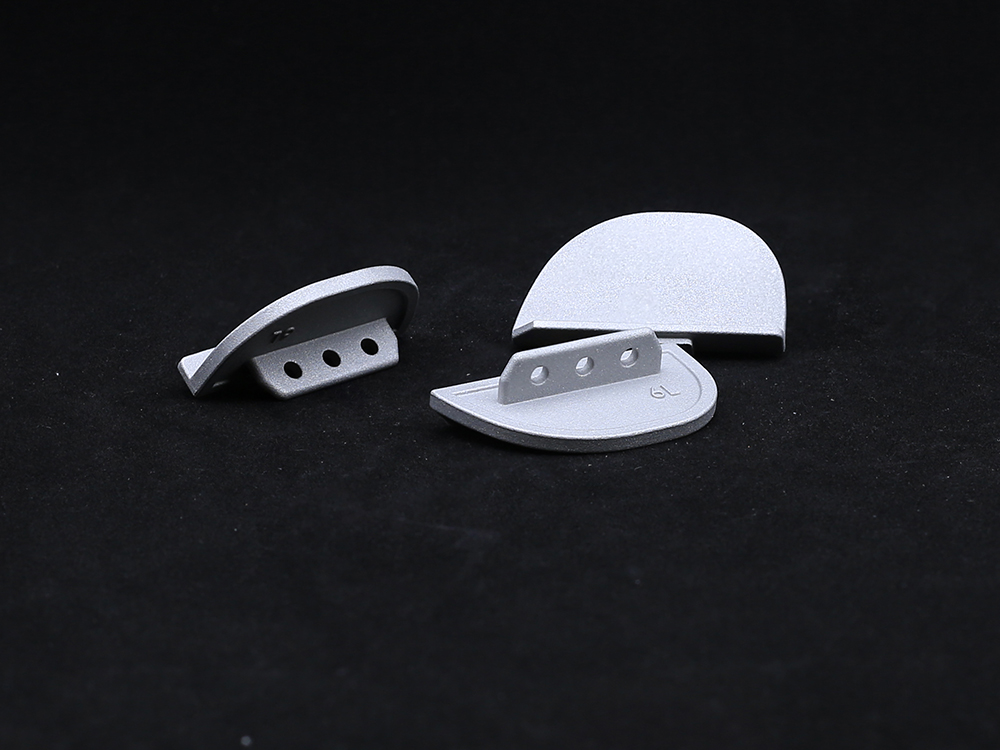
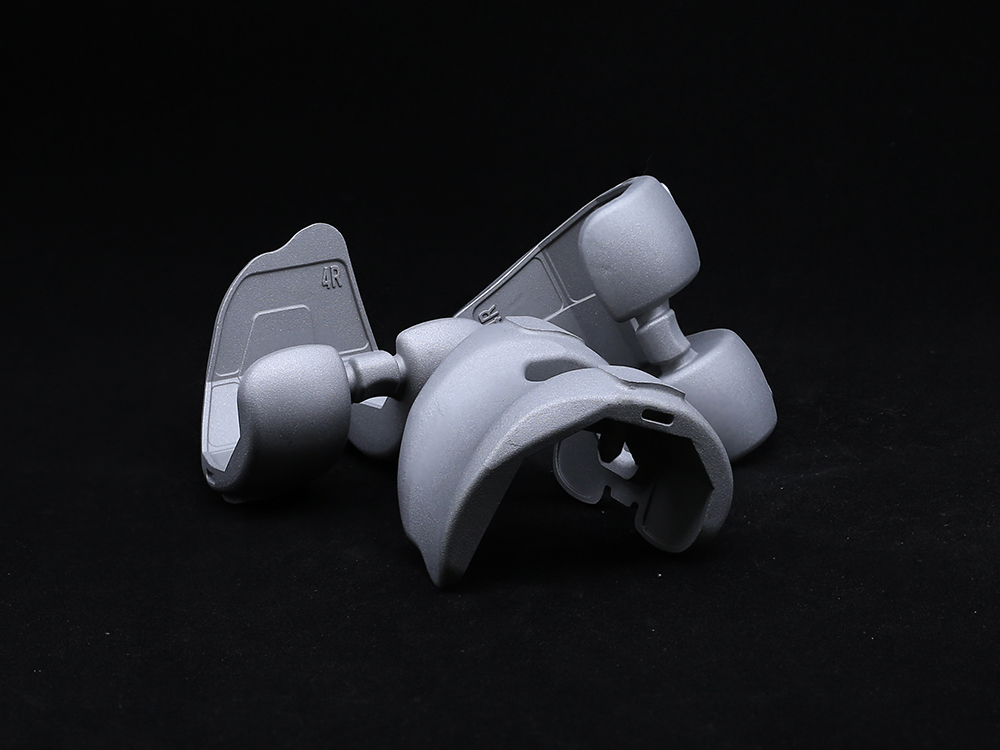
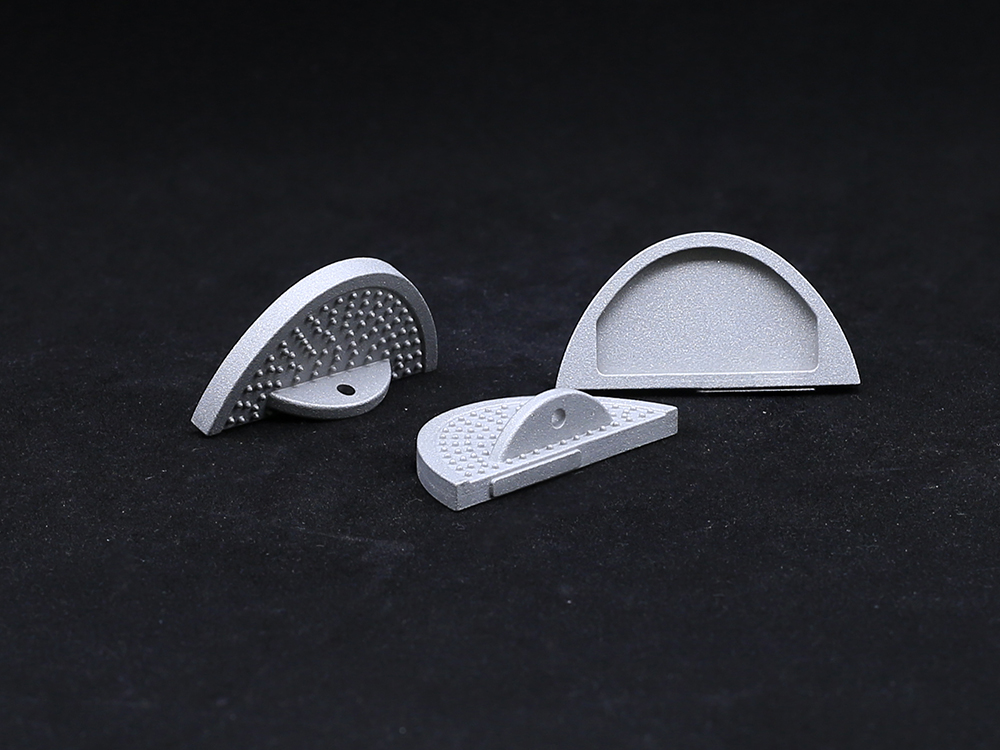
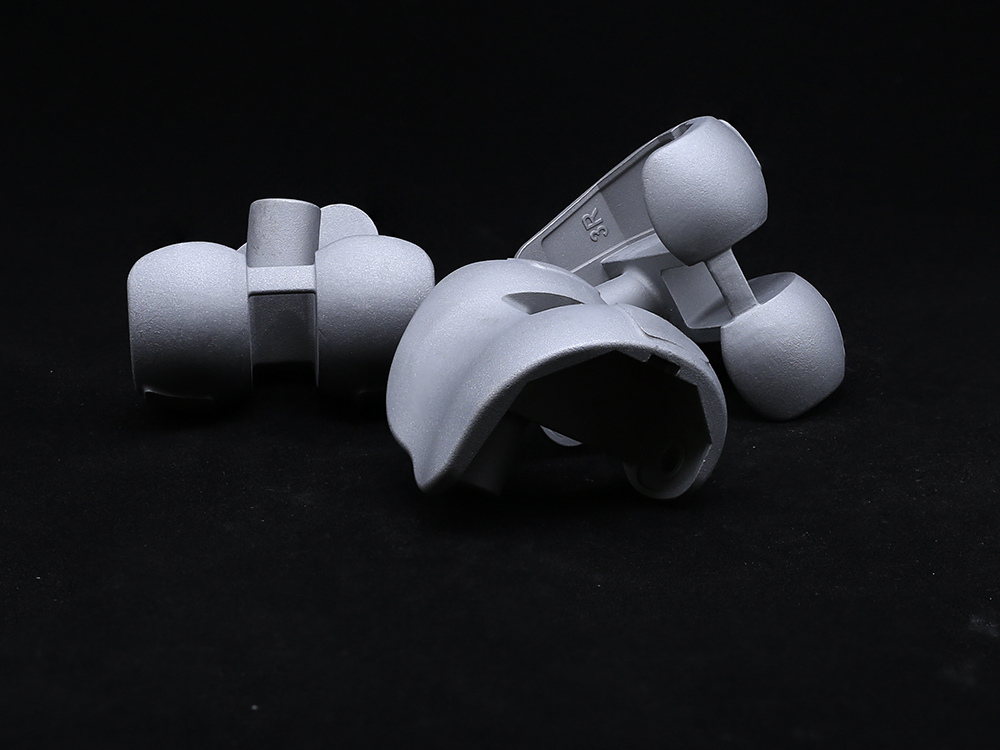
The outer surface of the acetabular cup anteversion usually adopts a hemispherical structure, which matches the curvature height of the human acetabular bone bed and can achieve precise implantation. The inner socket is customized according to the size of the femoral head prosthesis to ensure a stable ball and socket joint with the femoral head. At the same time, the outer surface of the Acetabular Cup is often designed with porous coatings, which can promote the growth of bone tissue, form biological fixation, enhance the stability of the connection between the prosthesis and the bone bed, and reduce the risk of loosening.
Material selection is the key to achieving wear resistance in Acetabular Cup
The current mainstream materials for acetabular cup size include titanium alloy, cobalt chromium molybdenum alloy, and ultra-high cross-linked polyethylene. Titanium alloy and cobalt chromium molybdenum alloy have excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility, and can withstand huge loads during hip joint movement; As an inner lining material, ultra-high cross-linked polyethylene has several times higher wear resistance than traditional polyethylene, which can reduce debris generated by friction, lower the probability of prosthesis loosening and bone resorption, and significantly extend the service life of the prosthesis.
The adaptability of the Acer Cup to surrounding tissues is crucial for postoperative flexibility
The rounded and smooth edge design of the reinforced tabular cup can avoid wear on surrounding ligaments and soft tissues; Rich in size specifications, personalized selection can be made based on the size and shape of the patient's hip socket to ensure that the hip joint can rotate flexibly within the normal range of motion after implantation, meeting the patient's daily movement needs such as walking and bending.
In clinical applications, ceramic acetabular cup have demonstrated significant advantages. The bio fixed Acetabular Cup achieves long-term stability through bone ingrowth and is suitable for patients with good skeletal conditions; The bone cement fixation type can quickly achieve stable fixation during surgery and is suitable for patients with osteoporosis. The combination of two fixation methods and different materials enables the Acetabular Cup to adapt to individual differences of various patients and improve the success rate of surgery. Meanwhile, its excellent wear resistance and stability significantly reduce the postoperative revision rate and improve the quality of life for patients.
In summary, the ceramic acetabular cup has become an indispensable core product in hip replacement surgery due to its anatomical design, high-performance material selection, good tissue adaptability, and rich clinical application advantages. It precisely meets the requirements of stability, wear resistance, and flexibility for surgery, providing reliable guarantees for patients to rebuild healthy hip joint function. It is of great significance for promoting the development of joint replacement technology and improving patients' postoperative quality of life.
Acetabular Cup FAQs
What is the role of Acetabular Cup in artificial joint replacement?
The acetabular cup, as the core component of hip prosthesis, is mainly used to replace the worn or diseased natural acetabulum of patients. Its design needs to closely adhere to the pelvic bones, achieve long-term stability through bone cement or biological fixation, and form a low friction motion interface with the femoral head prosthesis to ensure that the joint range of motion is close to physiological state.
How does the wear resistance of the Acetabular Cup affect the lifespan of the prosthesis?
Modern Acetabular Cups often use highly cross-linked polyethylene, ceramic, or metal materials to reduce wear rates through surface treatment techniques. For example, the wear rate of ceramics on ceramic composites is only 1/10 of that of traditional polyethylene, which can significantly reduce the generation of debris and avoid prosthesis loosening caused by bone resorption. Theoretically, the service life can reach more than 20 years.
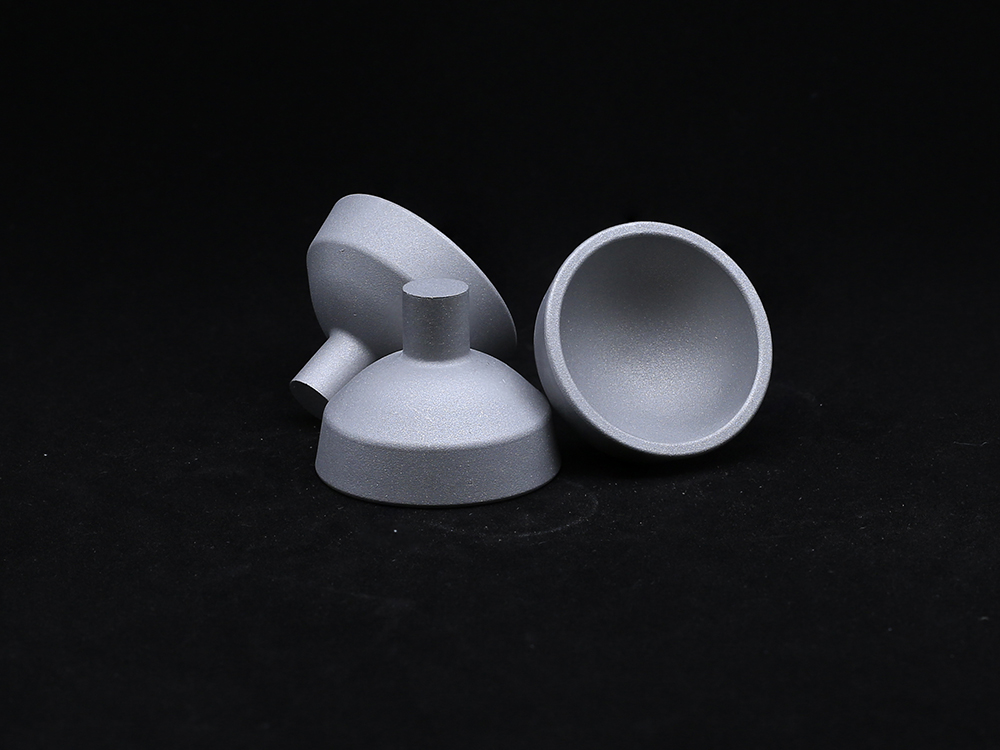
What are the technical differences between the dual action Acetabular Cup and traditional design?
The dual action structure adds a movable polyethylene liner within the Acetabular Cup, forming a "dual interface" motion mechanism. This design not only expands the joint movement angle, but also reduces the risk of dislocation through secondary buffering, especially suitable for young patients with high activity needs or osteoporosis population, but may increase the risk of wear caused by micro motion between components.
How to achieve bone ingrowth in the biological type of Acetabular Cup?
Its surface is usually coated with a three-dimensional porous layer (such as titanium mesh or tantalum metal), with a porosity controlled at 300-600 microns to promote bone cell growth. During the operation, initial stability is achieved through compression fitting technology. After 3-6 months, newly formed bone tissue will gradually grow into the pores, forming biological fixation. This bonding strength will exceed that of bone cement fixation over time.
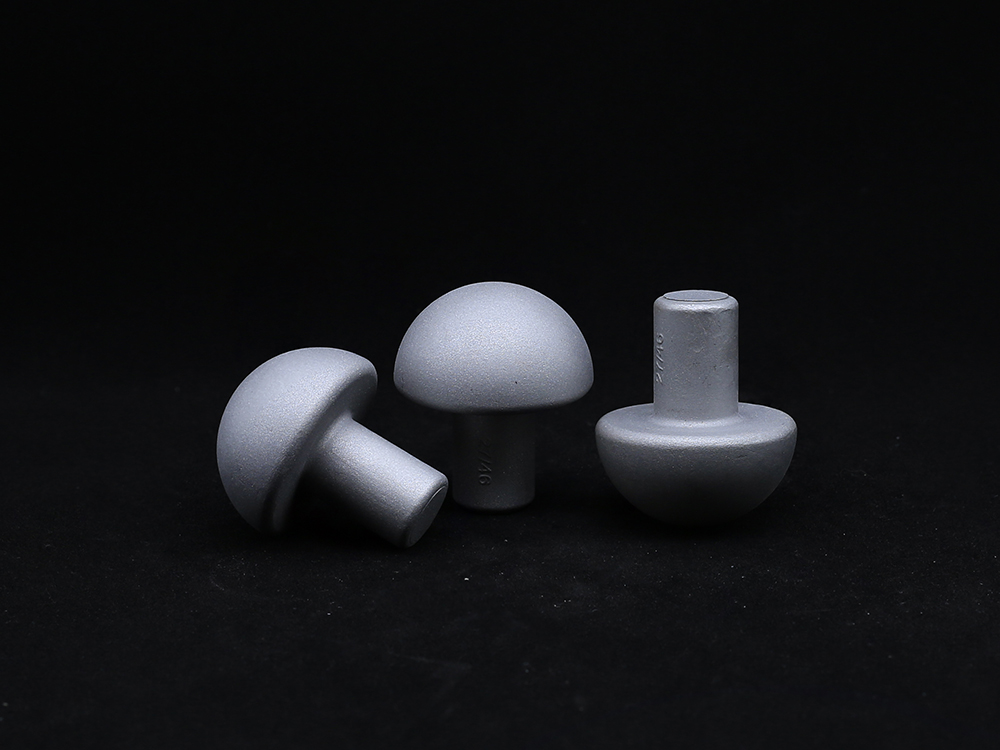
What is the biomechanical significance of the eccentricity design in the Acetabular Cup?
By adjusting the rotation center and edge curvature of the cup, the biomechanical axis of the hip joint can be accurately reconstructed. A reasonable eccentricity can balance the tension of surrounding soft tissues, avoid joint dislocation and reduce prosthesis impact, while optimizing the lever effect of the abductor muscle group, which directly affects the gait and joint load distribution of patients after surgery.
Get a Custom Solution!
Contact Us To Provide You With More Professional Services